What Are Healthspan and Healthgevity, and How Do They Differ from Lifespan and Longevity?
Aging isn’t just about adding years to our lives—it’s about ensuring those years are filled with vitality, independence, and freedom from chronic disease. While lifespan measures the total number of years we live, and longevity refers to our ability to live a long life, these terms don’t account for the quality of those years.
A longer lifespan can sometimes mean extended periods of poor health or reduced functionality. This is where the terms healthspan and healthgevity become crucial.
Healthspan refers to the length of time in life during which a person remains in good health, free from chronic conditions, disabilities, or significant physical decline. It focuses specifically on the quality of life during these years, ensuring that individuals can enjoy their added years with vitality and wellness. Healthgevity expands on the concept of healthspan, blending both quality and longevity. Healthgevity is about maximizing both the number of healthy years and the quality of those years.
As the global population ages, the distinction between simply living longer and living well has never been more important. Focusing on healthspan and healthgevity offers a more holistic framework for aging—one that prioritizes vitality, reduces disease, and aligns extended life with a higher quality of living.
The Growing Gap Between Lifespan and Healthspan
A global research study spanning from 2000 to 2019 revealed an increase in lifespan: from 79.2 to 80.7 years for women, and from 74.1 to 76.3 years for men. However, the study also uncovered a concerning trend: healthspan—the period of life spent in good health—did not increase at the same pace. In fact, the gap between lifespan and healthspan widened by 13%, reaching an average of 9.6 years, both globally and in the U.S.
Crucially, by analyzing data up until 2019, the researchers ensured their findings were not influenced by the COVID-19 pandemic, which could otherwise distort the results. This makes the study’s conclusions even more significant: while life expectancy continues to rise, many of these additional years are often spent in poor health. The increase in lifespan is not being mirrored by improvements in health, meaning that aging populations are increasingly burdened by disease and disability.
These findings have important implications for healthcare policies and practices. The widening gap between lifespan and healthspan calls for a renewed focus on not only extending life but also improving the quality of those years. It’s vital to prioritize healthspan alongside lifespan to ensure that longer lives are also healthier lives.
For more details, you can read the original research study here
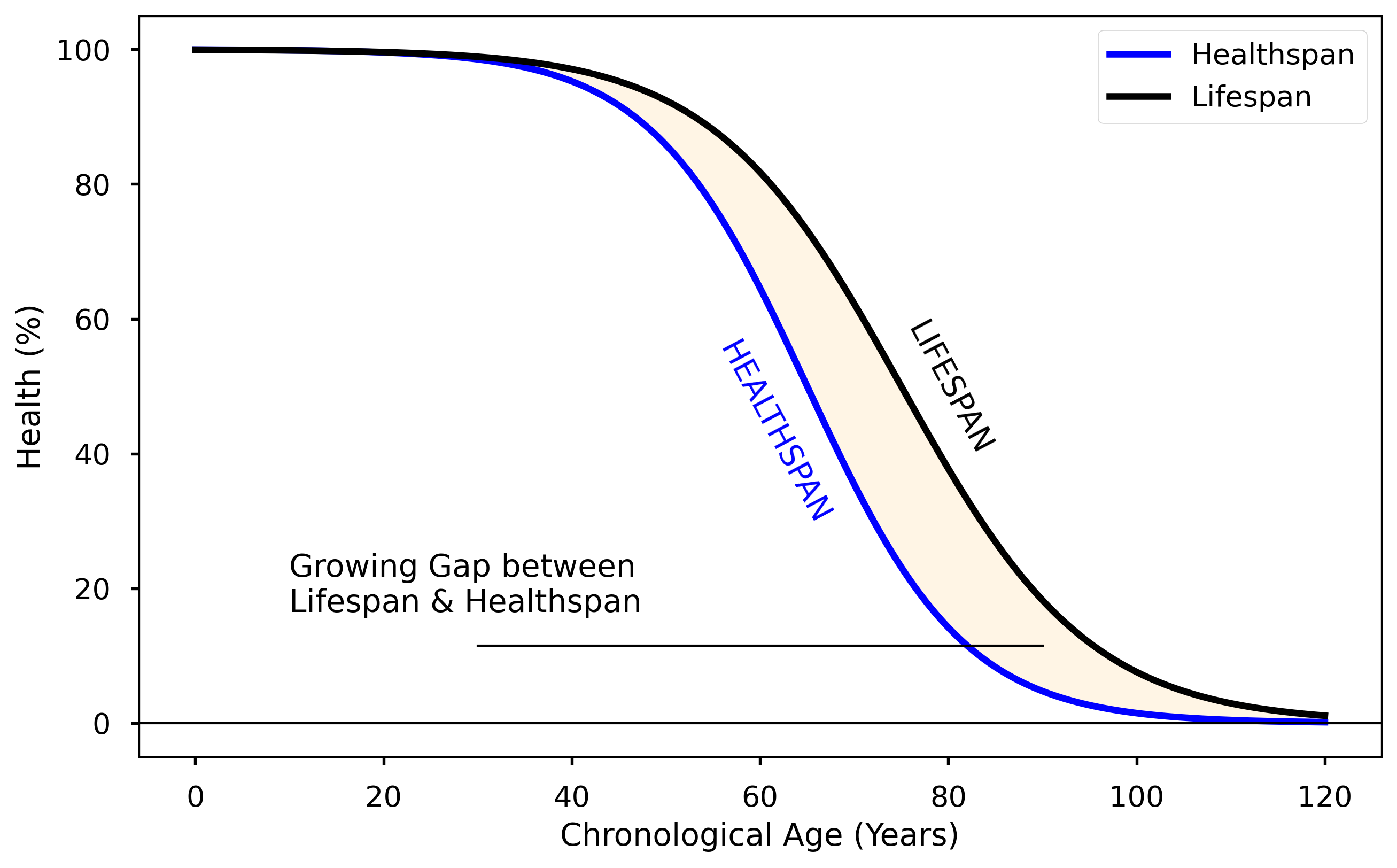
Graphical representation of the relationship between healthspan and lifespan, illustrating the widening gap between the two curves. The shaded region indicates the disparity between healthspan and lifespan, reflecting the increasing duration of impaired health prior to mortality.
Why Emotional and Mental Health Are Critical to Extending Healthspan and Healthgevity
Mental and emotional well-being play a pivotal role in extending both healthspan and healthgevity. Mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and cognitive decline associated with dementia significantly impact overall well-being. Alarmingly, these issues are often overlooked until they have reached advanced stages.
Serious mental health disorders can reduce life expectancy by 10 to 25 years—comparable to or even worse than the effects of smoking. Moreover, mental health issues are strongly linked to a higher risk of dementia. Research shows that 6% of individuals with mental health conditions develop dementia, compared to only 1.8% of those without.
The impact of poor mental health extends beyond life expectancy. It is also associated with chronic conditions, infectious diseases, poor self-care, and even an increased risk of suicide. In contrast, emotional well-being has been shown to improve recovery and survival rates, boost immune function, and lower the risk of cardiovascular disease.
On a biological level, mental health factors influence the very mechanisms that drive aging, including mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, and loss of proteostasis.
At Exaia, we recognize that emotional and mental health must be central to any holistic approach to aging. Proactively addressing mental health can help individuals maintain vitality, independence, and cognitive function, ensuring not just a longer life, but a healthier, more fulfilling one.
From Lifespan to Healthspan: The Evolution of Healthcare Towards Better Lives
The history of healthcare has evolved in stages, driven by technological, societal, and medical advancements. With each new phase, healthcare systems have shifted focus, addressing the pressing health challenges of the time. The journey from Healthcare 1.0 to Healthcare 4.0 reflects not only improvements in treating diseases but also the growing emphasis on extending Healthspan. Here’s an overview of the four main stages of healthcare evolution:
Healthcare 1.0: The Foundations of Modern Medicine (1800s – Early 1900s)
- Emergence of germ theory, revolutionizing our understanding of disease.
- Advancements in sanitation (clean water, sewer systems) and vaccination dramatically reduced infectious disease outbreaks.
This era laid the foundation for disease prevention and public health. The focus was primarily on combating infectious diseases, improving hygiene, and introducing vaccinations. However, the focus on healthspan (living well) and extending healthy years was minimal.
Healthcare 2.0: The Era of Mass Medicine (1900s – Late 20th Century)
- Breakthroughs such as the advent of antibiotics like penicillin and medical technologies such as X-rays.
- Growth of large hospitals and healthcare infrastructure to manage growing urban populations.
Healthcare during this period was predominantly curative. The focus was on treating illness rather than preventing it. The emphasis was on life expectancy, with little attention paid to the quality of those years, especially as aging populations faced chronic conditions.
Healthcare 3.0: The Digital Health Revolution (1980s – Early 21st Century)
- Introduction of electronic health records (EHRs) and telemedicine for better data management and remote care.
- Surge in evidence-based medicine, driving decisions based on data and research.
While Healthspan started to gain attention in this era, healthcare remained largely reactive—focused on treatment rather than prevention. The digital revolution made healthcare more efficient but did not fully address the underlying need for proactive measures to maintain health throughout life.
Healthcare 4.0: The Era of Smart, Connected, and Personalized Health (2020 – Present)
- The integration of AI, IoT and big data for continuous health monitoring and predictive analytics.
- Rise of personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to individuals based on genetic, behavioral, and environmental data.
In Healthcare 4.0, the focus has shifted significantly toward proactive health management,emphasizing Healthspan and Healthgevity—not just longer life, but a life lived in good health. By leveraging AI-powered solutions, wearable devices, and predictive analytics, healthcare systems are now capable of not only extending lifespan but also optimizing the quality of those years.
This stage is transforming the way we approach aging, by shifting from episodic to continuous care, where patient health is constantly monitored, and interventions are personalized. The goal is to optimize Healthspan—ensuring that individuals not only live longer but remain healthy, independent, and free from chronic disease for as many years as possible.
Comparison at a Glance:
| Stage | Key Technologies/Features | Primary Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare 1.0 | Germ theory, sanitation, vaccines | Public health and disease prevention |
| Healthcare 2.0 | Antibiotics, big hospitals, medical equipment | Mass medicine and curative care |
| Healthcare 3.0 | EHRs, telehealth, evidence-based medicine | Digitalization and efficiency |
| Healthcare 4.0 | AI, IoT, big data, personalized medicine, predictive analytics | Smart, connected, and proactive care |
Connecting Healthcare 4.0 to Healthspan and Healthgevity
The shift to Healthcare 4.0 is not just about extending lifespan; it’s about enhancing healthspan. Through emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and digital biomarkers, we are moving closer to a future where we can monitor and improve both physical and emotional/mental health, ensuring that added years are filled with vitality, independence, and freedom from debilitating disease.
At Exaia, we’re proud to be at the forefront of this transformation. Our advanced AI models for precision diagnostics, continuous monitoring, and digital biomarker technologies are helping to shape the future of healthcare.
How AI-Powered Software Solutions Are Revolutionizing Healthcare 4.0 for Emotional and Mental Health
AI-powered solutions are reshaping the landscape of mental, emotional, and neurological healthcare by enabling proactive, preventive, and personalized care. At Exaia, we are leading the way in integrating AI, digital biomarkers, and machine learning to deliver real-time, actionable insights that not only enhance emotional well-being but also empower the early detection and ongoing management of neurodegenerative and psychiatric conditions.
Our innovative AI SaaS solutions address key areas of proactive care:
- Early Detection & Risk Assessment: By identifying early signs of susceptibility to neurodegenerative and psychiatric conditions, we enable timely, personalized interventions that promote long-term well-being and minimize risks.
- Precision Diagnostics & Comorbidity Management: Utilizing biomarkers, we ensure accurate diagnosis, even in complex cases with overlapping symptoms. This precision allows for individualized treatment plans and better management of co-occurring conditions, enhancing overall care effectiveness.
- Continuous Monitoring & Treatment Optimization: We provide ongoing monitoring of health status and treatment outcomes, ensuring that interventions are continuously optimized based on real-time data, supporting sustained mental and neurological health over time.
By harnessing these technologies, we’re moving from reactive care to a more proactive approach, offering tailored interventions that help individuals maintain optimal mental and emotional health throughout their lives.
For more information, visit CYMO Use Cases.
Curious How CYMO’s Digital Biomarkers & AI Models Can Work for You?
Experience the future of emotional and mental health diagnostics with CYMO’s advanced digital biomarkers and AI models. See how we’re revolutionizing real-time health monitoring and get a firsthand look at the difference it can make.